Nilay, the CEO of Advanced Defence Systems, a defence products manufacturing firm prided himself on two things. The technologically advanced defence products they were manufacturing for Indian armed forces, and the cybersecurity measures they had in place to protect their own systems – firewalls, antivirus software, data protection, just to name a few. To ensure that they stay ahead of the curve, ADS had hired external consultants to conduct regular penetration tests to ensure they had data security.
ADS’s products were gaining market share. Their continued success, however, brought its own challenges. When everything appeared hunky dory, Seema Singh, ADS’ CISO (Chief Information Security Officer) reported to Nilay a major data breach that compromised the database security, endpoint security and posed other cyber threats.
Anyone could have been their adversary – venomous terrorists, malicious subversives, agenda-chasing political criminals, surreptitious state-backed foreign intelligence services, curious computer hackers, evil commercial competitors, dishonest insiders, disgruntled staff, trusted but careless business partners, or rogue administrators.
Nilay knew that he could not allow this to be repeated. In a review of their defensive posture with Seema, She suggested that it was time to go for Red teaming – a simulated cyber-attack, designed to test an organization’s security defenses to identify vulnerabilities that an attacker could exploit to gain unauthorized access to an organization’s systems or data. Nilay made up his mind and wanted to give it a try. Seema brought together a team of ethical hackers and other IT professionals.
The team proposed its plan. It involved the following important steps:
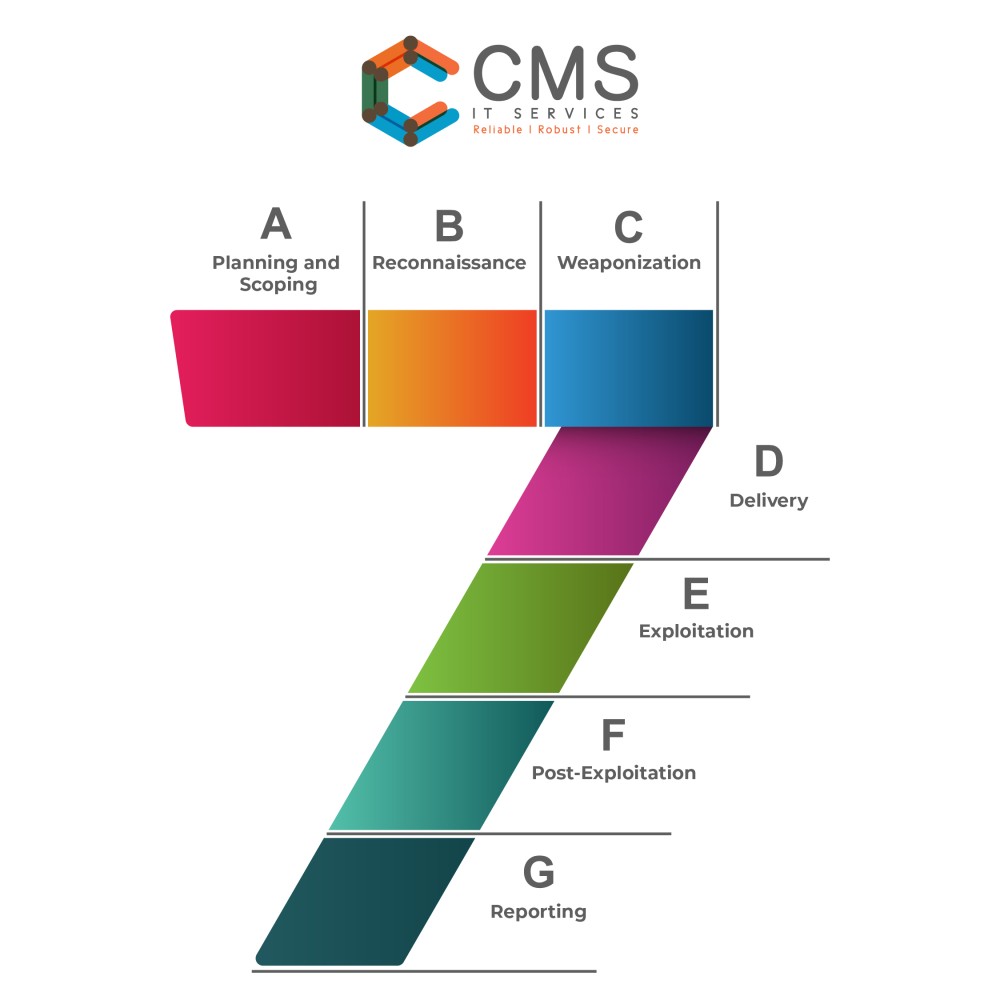
- Planning and Scoping: The first step in red teaming was to define the scope of the exercise and plan the attack. This involved identifying the assets that need to be protected and developing a strategy for the attack.
- Reconnaissance: They conducted reconnaissance to gather information about the organization’s systems and networks. This involved scanning for vulnerabilities and identifying potential targets.
- Weaponization: Once the reconnaissance was completed, the red team developed the attack tools and techniques that will be used to exploit vulnerabilities in the organization’s defenses.
- Delivery: The red team delivered the attack. They used social engineering techniques to gain access to the organization’s systems or networks.
- Exploitation: The red team exploited vulnerabilities in the organization to gain access to sensitive data and systems.
- Post-Exploitation: Now the red team just had to maintain access to the organization’s systems and networks – installed backdoor and other malicious software.
- Reporting: The red team documented the results and provided a report to the management. It had recommendations for improving the organization’s security defenses.
By simulating a real-world cyber-attack, ADS was able to identify weaknesses that could be exploited by real-world attackers. Technology is not static. It keeps on evolving. As defensive postures evolve, so do attacks and attackers.
Nilay agreed with Seema’s suggestion to carry our red teaming regularly and stay ahead of the curve by maintaining effectiveness of ADS’ security defences and keeping them state of the art.
How about you? Is your cyber defence up to date?
If you have queries related to 𝘾𝙮𝙗𝙚𝙧 𝙎𝙚𝙘𝙪𝙧𝙞𝙩𝙮, reach out to our in-house Cyber Security experts. They are happy to hear from you info@cmsitservices.com. You could also reach out to us on our website https://www.cmsitservices.com/contact-us/.